This math topic focuses on the application of the Pythagorean theorem to solve for missing sides in right triangles, using integer values. It emphasizes finding the value of one side when the lengths of the other sides are known, enlarging upon the foundational principles of Pythagoras' theorem. The problems are designed to enhance skills in manipulating algebraic equations derived from the theorem, specifically \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \), where 'a', 'b', and 'c' represent the sides of the triangle, with 'c' typically being the hypotenuse. This set of problems is suitable for reinforcing understanding of the theorem in practical scenarios.
Work on practice problems directly here, or download the printable pdf worksheet to practice offline.
morePythagorean Equation from Variables - Length of Side (Integer) Worksheet

| Math worksheet on 'Pythagorean Equation from Variables - Length of Side (Integer) (Level 2)'. Part of a broader unit on 'Pythagoras - Foundations' Learn online: app.mobius.academy/math/units/pythagoras_foundations/ |
1
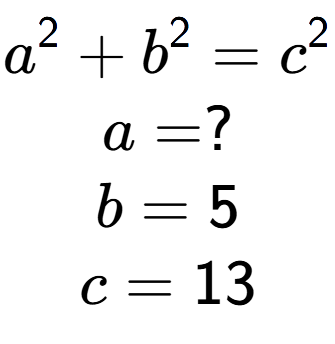
| Find the value of 'a' in this equation |
a
| a = 8 |
b
| a = 14 |
c
| a = 13 |
d
| a = 12 |
e
| a = 7 |
f
| a = 16 |
2

| Find the value of 'b' in this equation |
a
| b = 5 |
b
| b = 8 |
c
| b = 156 |
d
| b = 4 |
e
| b = 7 |
f
| b = 6 |
3
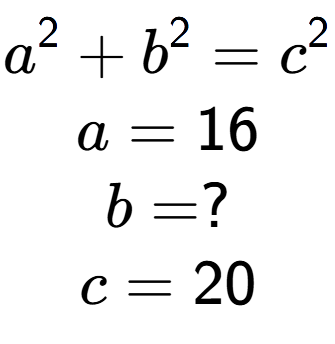
| Find the value of 'b' in this equation |
a
| b = 20 |
b
| b = 13 |
c
| b = 320 |
d
| b = 15 |
e
| b = 11 |
f
| b = 12 |
4
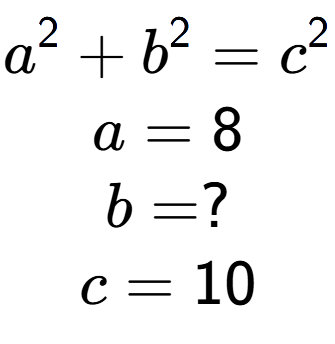
| Find the value of 'b' in this equation |
a
| b = 8 |
b
| b = 5 |
c
| b = 18 |
d
| b = 6 |
e
| b = 80 |
f
| b = 7 |
5

| Find the value of 'b' in this equation |
a
| b = 10 |
b
| b = 12 |
c
| b = 6 |
d
| b = 16 |
e
| b = 9 |
f
| b = 7 |
6

| Find the value of 'b' in this equation |
a
| b = 8 |
b
| b = 4 |
c
| b = 16 |
d
| b = 7 |
e
| b = 11 |
f
| b = 5 |
7

| Find the value of 'a' in this equation |
a
| a = 4 |
b
| a = 12 |
c
| a = 10 |
d
| a = 9 |
e
| a = 180 |
f
| a = 6 |