This math topic focuses on applying the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the length of missing sides in right-angled triangles, where dimensions are given in scaled values. Each problem presents a triangle with specific side lengths and requires finding the length of an unknown side, with answers listed in decimal format. This set of exercises is intended to develop and test a student's ability to work with Pythagorean triples and understand the relationship between the sides of right-angled triangles in various scaled scenarios.
Work on practice problems directly here, or download the printable pdf worksheet to practice offline.
morePythagorean Triples (Scaled) - Length of Side Worksheet

| Math worksheet on 'Pythagorean Triples (Scaled) - Length of Side (Level 2)'. Part of a broader unit on 'Pythagoras - Practice' Learn online: app.mobius.academy/math/units/pythagoras_practice/ |
1
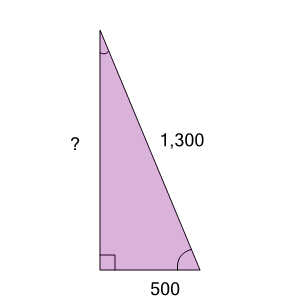
| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 800 |
b
| 1,300 |
c
| 1,200 |
d
| 6,500 |
e
| 1,400 |
f
| 700 |
2

| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 37,500 |
b
| 2,000 |
c
| 2,600 |
d
| 1,600 |
e
| 1,700 |
f
| 2,500 |
3
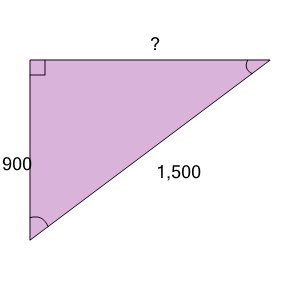
| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 1,300 |
b
| 1,200 |
c
| 600 |
d
| 13,500 |
e
| 800 |
f
| 900 |
4
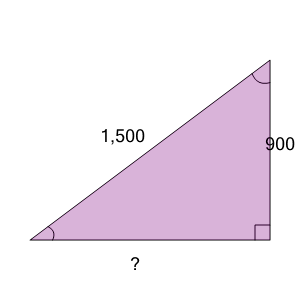
| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 600 |
b
| 1,500 |
c
| 1,100 |
d
| 1,600 |
e
| 1,000 |
f
| 1,200 |
5
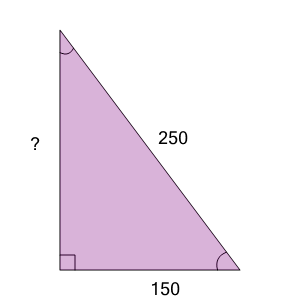
| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 160 |
b
| 200 |
c
| 100 |
d
| 3,750 |
e
| 120 |
f
| 180 |
6
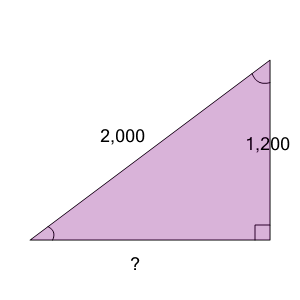
| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 1,700 |
b
| 1,100 |
c
| 1,600 |
d
| 1,400 |
e
| 24,000 |
f
| 2,000 |
7

| Find the length of the missing side as a decimal value based on the Pythagorean theorem |
a
| 2,400 |
b
| 100 |
c
| 160 |
d
| 110 |
e
| 190 |
f
| 130 |